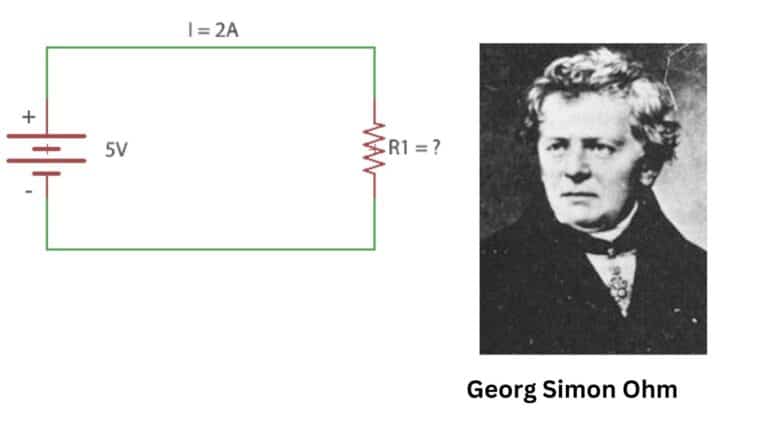
When current flows trough a material, the flow is resisted. This behavior is known as resistance. So, resistance is the property or ability to resist the flow of current. This is represented by R. And the material which have resistance property is called resistor. The unit of resistance is Ohm and represented by ῼ.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Factors Affect Resistance?
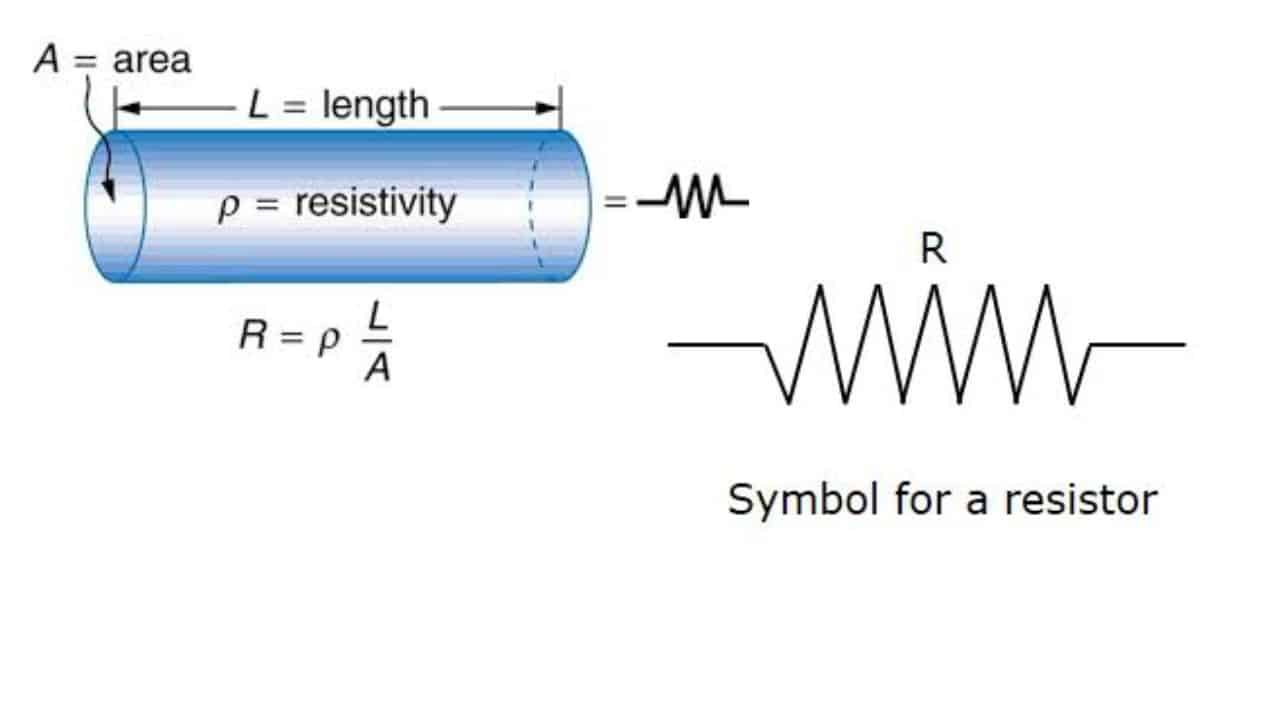
Resistance depends on materials, its temperature, length, area of cross section. Though all these factors can vary simultaneously During calculating resistance, we not consider all these factors at a time. First we calculate the effect of changing length and cross sectional area, assuming constant temperature. Then calculate the effect of changing temperature.
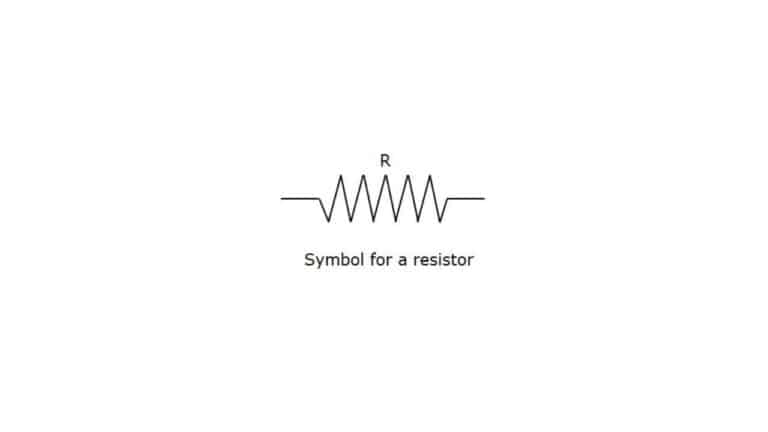
Dependence Factors of Resistance At Constant Temperature
Dependence of Resistance on Temperature
Conductor and semiconductor shows contrary behavior in changing temperature. The thumb rule is, in conductor resistance increases with temperature but not proportionately. In semiconductor resistance decreases with temperature increase. The equation of resistance and temperature with a low range is following:
RT=R0[1+α(T-T0)]
Here,
RT = is resistance at temperature T
R0 = is resistance at temperature T0
α = Temperature coefficient of resistance. Its value is positive for conductor and negative for semiconductor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is resistance?
Resistance is the ability to resist the flow of electric current.
What is the SI unit of resistance?
The SI unit of resistance is Ohm (ῼ).
On what factors resistance depends?
Resistance depends on material, temperature, length and cross-sectional area.
What is the relation between length and resistance?
Resistance is proportional to length.
What is the relation between cross sectional area and resistance?
Resistance is inversely proportional to cross sectional area.
Resistance is inversely proportional to cross sectional area.
No, this is true for conductor only. In semiconductor resistance decreases with temperature.
That’s all for today!
In the next article we will do some mathematical calculation on resistance.
One Comment