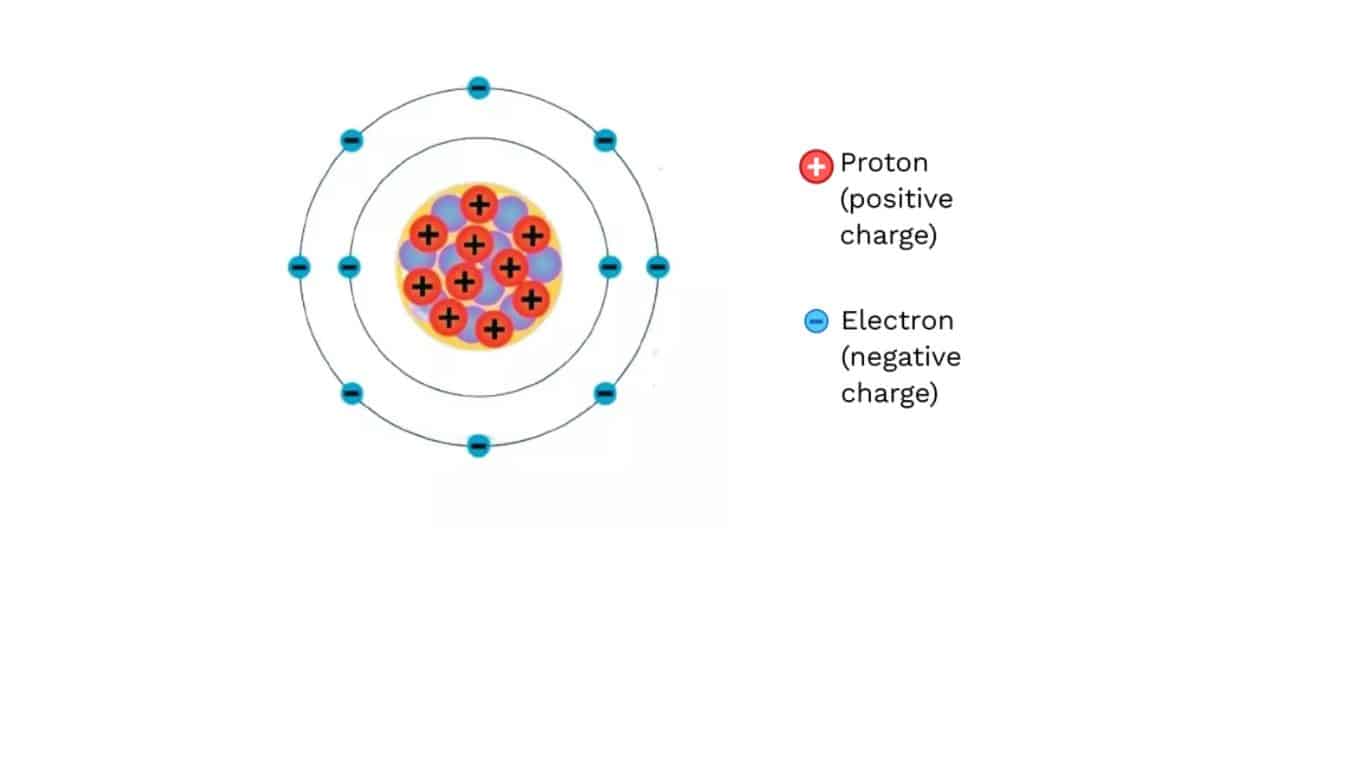
Atom consists of three main particles electron, proton and neutrons. Among these particles electron and protons have charge property. But neutron has not charge property. So, now if I asked you what is electric charge? The answer will be electric charge is the fundamental properties of electron and proton. Charges are affected by electric and magnetic field.
Table of Contents
ToggleSo, electric charge is the basic property of elementary particles which govern atom and affected by electric and magnetic field.
What Is the Unit of Charges?
The unit of charges is Coulomb. It came from the name of scientist C.A. Coulomb. It is expressed by C. 1 C = 1 Ampere second.
Types of Charges?
A Proton and A neutron have the same amount of charges. Protons charges are positive, whereas electrons charges are negative. So, two types of charges are present, one is positive and other is negative.
How Charges Are Formed?
We have already known that only electron and proton carry charges. The number of charges in a proton is +1.6×10 ^-19 C and it is represented by +1e. The number of charges in an electron is –1.6×10 ^-19 C and it is represented by -1e. Number of electron and proton in an atom in normal condition is equal. So, an atom is charge free. But if atom is excited or conflict with other atoms it donates or receive electrons. As a result, number of electrons and protons are imbalanced. Therefore, charges are formed in atom. Now, we can say that charges are formed in a material when the number of protons and electrons are imbalanced in it. As proton can not transfer from one material to other, simply we can say that charges are created by the transfer of electrons. When an atom receives electrons, it forms negative charge. When it denotes electrons, positive charge is formed. When receive 1 electron, –1.6×10 ^-19 C charges are formed. By receiving 2 electrons -2*1.6×10 ^-19 C charges are formed. Similarly, by denoting 1 electron +1.6×10 ^-19 C charges are formed. By denoting 2 electrons +2*1.6×10 ^-19 C charges are formed. Charges are formed only integer multiple of electron charge 1.6×10 ^-19 C. This is known as quantization. We learn this more later of this article. Hopefully you understand, how charges are formed in a material.
Basic Properties of Electric Charge
In this section, we will learn about basic properties of electric charge. Additivity, conservation and quantization are the three basic properties of electric charge. Let’s discuss more about these properties.
Additive Property of Electric Charge
Total charge of a system is the sum of the charges of individual particles in the system. Suppose a system has three particles, they consist of three charges q1, q2, and q3. So, the total charge of the system is algebraic sum of these three charges.
Q=q1+q2+q3
Electric charges are scalar quantities, they have only magnitude but no direction. So, they can be treated as real numbers. q1, q2, q3 can be positive or negative. Therefore, we need to consider the sign of charges during additive operation.
Total charges of a system containing n particles can be expressed as:
Q=q1+q2+q3+……..+qn
Conservation Property of Electric Charge
The principle of charge conservation says that charge can not be created or destroyed, it only transfers from one body to another.
For example, when a charged object is placed in contact with another charged free object, charged object will provide charge two charge free object. This exchange process will continue until there charges will be equal.
Here we see that no new charges are created, only transferred from object to object. This is the law of conservation of electric charge.
Quantization of Electric Charge
Though in above section, we briefly discussed about charge quantization. In this section, we will explain it.
The main theme of charge quantization is charge can not be formed in any numbers. It only formed as the integer multiple of an electron charge 1.6×10 ^-19 C. That means number of charges can be +1e, -1e, +2e, -2e, +3e, -3e and so many. But it can not be formed as +1.5e, +1.1e or other fraction of e. Remember that here e represents the number of charges of an electron 1.6×10 ^-19 C.
So according to charge quantization, number of charges, Q=+ne or -ne.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Electric Charge
What is electric charge?
Electric charge is the basic property of elementary particles which govern atom and affected by electric and magnetic field.
What is the SI unit of electric charge?
SI unit of electric charge is Coulomb (C)
How electric charges are formed?
Electric charges are formed by the transfer of electrons.
What are the three basic properties of electric charge?
Three basic properties of electric charge are additivity, quantization, and conservation.
What are the types of electric charge?
There are two types of electric charge, positive and negative.
Who discovered electric charge?
Benjamin Franklin.
Can charge be formed by any numbers?
No, charge can only be formed by integer multiple of electron charge.
The time has come to say goodbye for today. Hope this article enriches your knowledge about charge, it’s type and properties. You are advised to visit our website in regular intervals to keep up with our latest information.
0wlsaj
syiike
ss6luu
3tq4d4